Biological Sciences
BSc (Hons)
UCAS code: C900
Start dates: September 2024 / September 2025
Full time: 3 years, 4 years sandwich
Part time: 6 years
Location: Headington, Headington (Marston Road site)
Department(s): Department of Biological and Medical Sciences
Overview
Does the living world fascinate you? Are you interested in the innovation and commercial utilisation of bioscience knowledge?
This course offers you the flexibility to discover what kind of biologist you want to be. You will have the freedom to choose the topics you want to study across the breadth of biology; whether your interests lie in the environment, animal behaviour, plants, molecular biosciences, or span all areas.
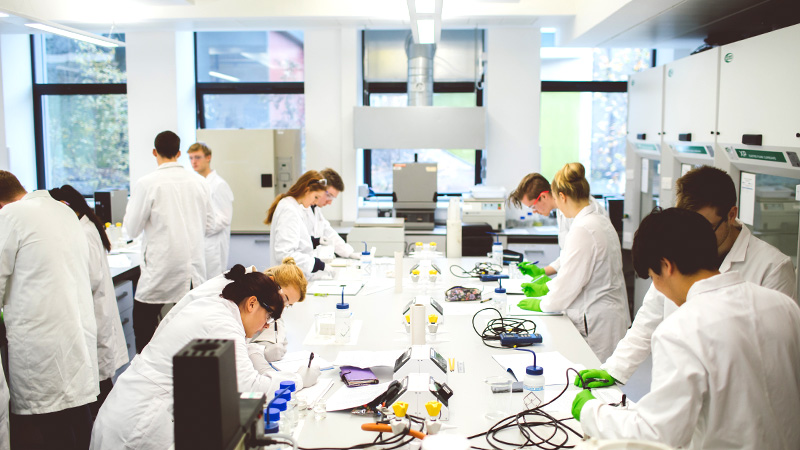
We'll support you to gain the skills and confidence employers want. This starts with understanding scientific theories and how they are used in the real world and continues through your assessments that focus on communication skills including presentations, report writing and teamwork. You will develop the practical skills used in research and commercial labs, including data handling and computing. Our labs are equipped with industry standard technology, including 3D electron microscopes.
We’re proud of our nurturing environment with good connections between staff and students. You’ll benefit from research-active tutors and small group sizes.
Why Oxford Brookes University?
-
Amazing facilities
A range of teaching labs with industry-standard equipment, including bioinformatics and research labs for projects.
-
Course flexibility
Tailor the course to suit your interests. You can choose from a broad range of modules, starting with a foundation year if you need it, taking a year in industry or opting for our integrated master's.
-
Employment success
We offer modules to help you identify interesting career paths and to develop your professional skills. These are supported with the opportunity to gain work experience through a placement year, a work experience module or research project.
-
Strong industry links
We're able to offer great guest speakers and work experience opportunities due to our excellent industry links. These include biotechnology, conservation, NHS Trusts, start-ups as well as local bioscience companies and top research centres.
-
International exchanges
Are you ready to expand your horizons? Do you want to explore a different culture? You may be able to spend a semester or a year studying and living in a different country.
-
Free language courses
Free language courses are available to full-time undergraduate and postgraduate students on many of our courses, and can be taken as a credit on some courses.
-
Study abroad
You may be able to go on a European or international study exchange while you are at Brookes. Most exchanges take place in the second year. Although we will help as much as we can with your plans, ultimately you are responsible for organising and funding this study abroad.
Course details
Study modules
Please note: As our courses are reviewed regularly as part of our quality assurance framework, the modules you can choose from may vary from those shown here. The structure of the course may also mean some modules are not available to you.
Careers
Our graduates enjoy good career prospects working with a range of organisations. Employers have included hospitals, biotech companies e.g. UK Biocentre, zoos and conservation trusts.
The skills we give you as a graduate also prepare you for graduate jobs outside the biosciences. Popular employers/roles include:
- bioscience, biotechnology, and healthcare
- environmental agencies and consultancies
- food and drink industries
- government or charity-funded laboratories
- universities and research institutes
- clinical trials coordinator
- teacher
- procurement officer
- sequencing and validation scientist
- microbiologist
- lab technician
- biotechnologist
- science communication.
Many graduates carry on their studies with us or other institutions. Our MSc Conservation Ecology and MSc Genetics and Genomics have been particularly popular. Some continue onto PhDs, including internally funded PhDs.
Student profiles
Our Staff
Dr Casper Breuker
"My teaching strongly reflects both my multidisciplinary research interests as well as my commitment to shaping and influencing curriculum development within the department."
Read more about CasperRelated courses
Entry requirements
Wherever possible we make our conditional offers using the UCAS Tariff. The combination of A-level grades listed here would be just one way of achieving the UCAS Tariff points for this course.
Standard offer
UCAS Tariff Points: 104
A Level: BCC
IB Points: 29
BTEC: DMM
Contextual offer
UCAS Tariff Points: 88
A Level: CCD
IB Points: 27
BTEC: MMM
Specific entry requirements
A Level: Including one A Level or a comparable Level 3 qualification in a science subject (e.g. Physical Education, Biology, Chemistry, Maths, Physics, Psychology).
If you do not have a background in science, we encourage you to consider our Life Sciences Foundation year.
Please also see the University's general entry requirements.
English language requirements
Please see the University's standard English language requirements.
Pathways courses for international and EU students
If you do not meet the entry requirements for this degree, or if you would like more preparation before you start, you can take an international foundation course. Once you enrol, you will have a guaranteed pathway to this degree if you pass your foundation course with the required grades.
If you only need to meet the language requirements, you can take our pre-sessional English course. You will develop key language and study skills for academic success and you will not need to take an external language test to progress to your degree.
English requirements for visas
If you need a student visa to enter the UK you will need to meet the UK Visas and Immigration minimum language requirements as well as the University's requirements. Find out more about English language requirements.
Credit transfer
Many of our courses consider applications for entry part-way through the course for students who have credit from previous learning or relevant professional experience.
Find out more about transferring to Brookes. If you'd like to talk through your options, please contact our Admissions team.
Terms and Conditions of Enrolment
When you accept our offer, you agree to the Terms and Conditions of Enrolment. You should therefore read those conditions before accepting the offer.
International qualifications and equivalences
How to apply
Application process
Full time international applicants can also apply through UCAS
Tuition fees
Questions about fees?
Contact Student Finance on:
Tuition fees
Please note, tuition fees for Home students may increase in subsequent years both for new and continuing students in line with an inflationary amount determined by government. Oxford Brookes University intends to maintain its fees for new and returning Home students at the maximum permitted level.
Tuition fees for International students may increase in subsequent years both for new and continuing students.
The following factors will be taken into account by the University when it is setting the annual fees: inflationary measures such as the retail price indices, projected increases in University costs, changes in the level of funding received from Government sources, admissions statistics and access considerations including the availability of student support.
How and when to pay
Tuition fee instalments for the semester are due by the Monday of week 1 of each semester. Students are not liable for full fees for that semester if they leave before week 4. If the leaving date is after week 4, full fees for the semester are payable.
- For information on payment methods please see our Make a Payment page.
- For information about refunds please visit our Refund policy page
Financial support and scholarships
Additional costs
Please be aware that some courses will involve some additional costs that are not covered by your fees. Specific additional costs for this course are detailed below.
You will need to buy some basic personal protection equipment for laboratory practicals (lab coat, safety glasses), at a cost of around £25.
Information from Discover Uni
Full-time study
Part-time study
Programme changes:
On rare occasions we may need to make changes to our course programmes after they have been
published on the website. For more information, please visit our
changes to programmes page.